62nd National Congress of the Italian Society of Rheumatology
Vol. 77 No. s1 (2025): Abstract book of the 62th Conference of the Italian Society for Rheumatology, Rimini, 26-29 November 2025
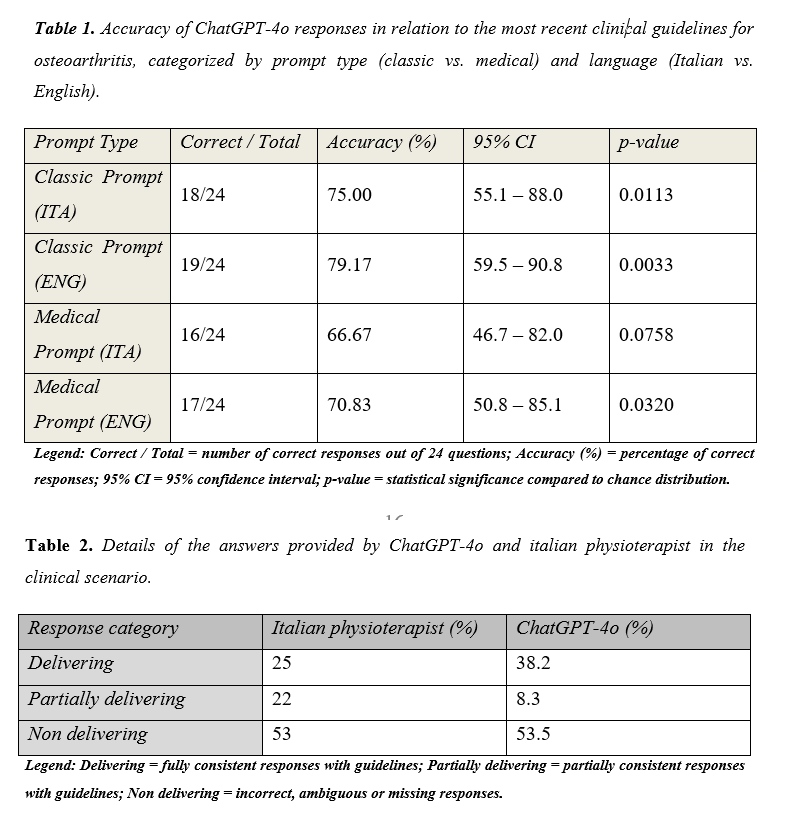
PO:38:283 | Accuracy of chatgpt 4 omni in providing clinical recommendations in musculoskeletal care: a valuable support for clinicians and patients?
Dario Taborelli1, Silvia Negro1, Federico Padovani2, Tiziano Innocenti1|3, Stefano Salvioli1 | 1DINOGMI, Università di Genova, Savona; 2Dipartimento di Neuroscienze e Riabilitazione, Università di Ferrara; 3GIMBE Foundation, Bologna, Italy
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Published: 26 November 2025
84
Views
0
Downloads