Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial lung disease related to systemic autoimmune myopathies: a narrative review
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 5 April 2023
Authors
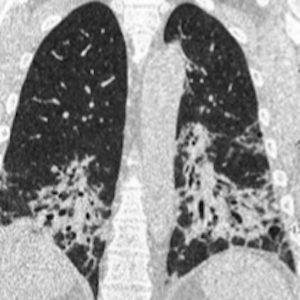
Systemic autoimmune myopathies (SAMs) are rare diseases that lead to muscle inflammation and may be associated with a variety of systemic manifestations. Although there is great heterogeneity in the spectrum of extra-muscular involvement in SAMs, interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most frequent lung manifestation. SAM-related ILD (SAM-ILD) presents significant variations according to geographic location and temporal trends and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Several myositis autoantibodies have been discovered over the last decades, including antibodies targeting aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes, which are associated with a variable risk of developing ILD and a myriad of other clinical features. In this review, the most relevant topics regarding clinical manifestations, risk factors, diagnostic tests, autoantibodies, treatment, and prognosis of SAM-ILD are highlighted. We searched PubMed for relevant articles published in English, Portuguese, or Spanish from January 2002 to September 2022. The most common SAM-ILD patterns are nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and organizing pneumonia. The combination of clinical, functional, laboratory, and tomographic features is usually sufficient for diagnostic confirmation, without the need for additional invasive methods. Glucocorticoids remain the first-line treatment for SAM-ILD, although other traditional immunosuppressants, such as azathioprine, mycophenolate, and cyclophosphamide have demonstrated some efficacy and, therefore, have an important role as steroid-sparing agents.
Supporting Agencies
This work was supported by Brazilian Society of RheumatologyHow to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.











