ORAL COMMUNICATIONS - TOWARDS EULAR 2026 (I)
6 October 2025
2025: Prova Issue
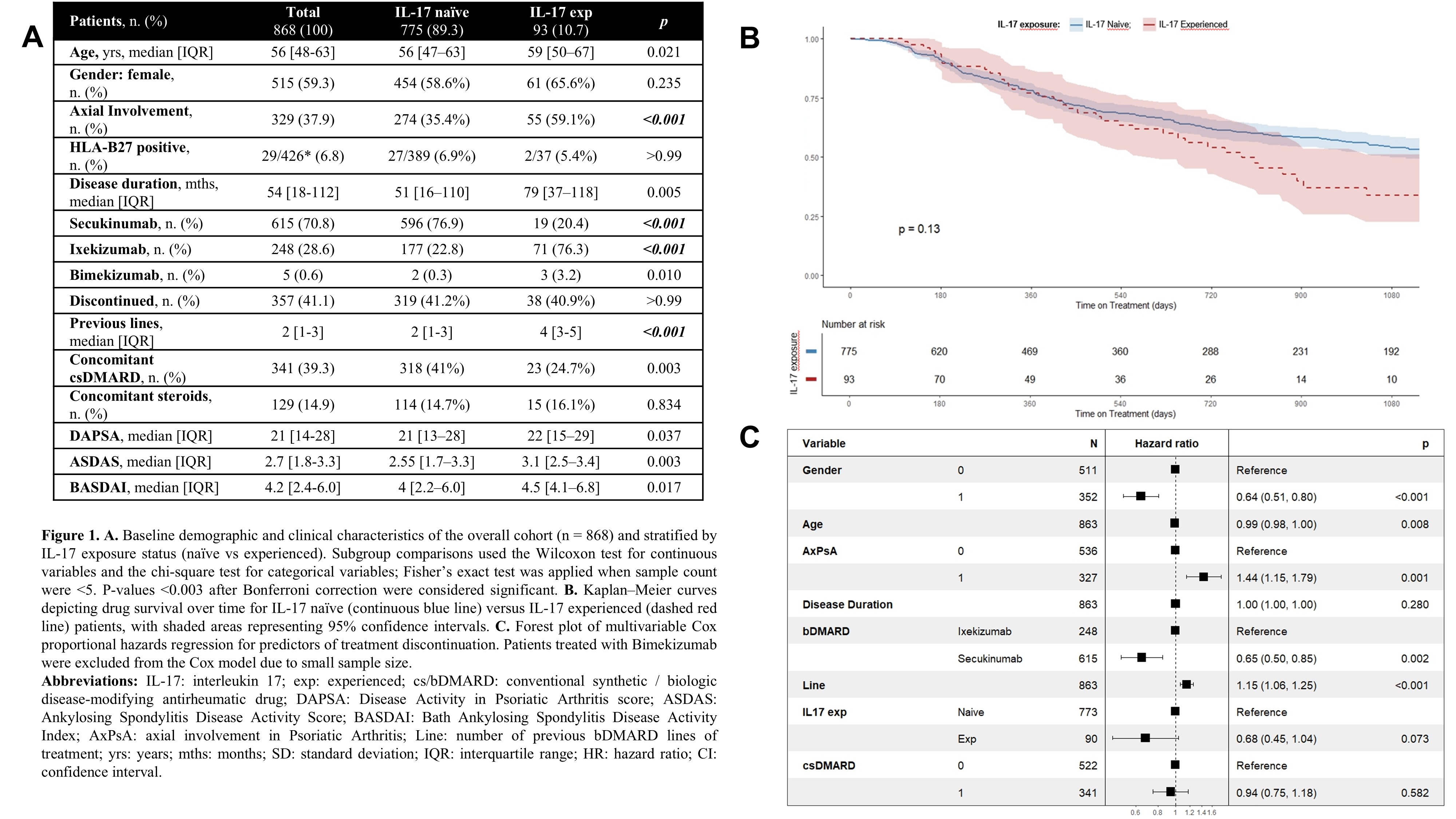
PO:01:004 | Real-world retention of IL-17 inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis: impact of prior IL-17 exposure across multiple treatment lines in the “birra” multicentre cohort
Valentino Paci1, Alarico Ariani2, Eleonora Celletti3, Alberto Lo Gullo4, Camilla Mazzanti5, Valeria Nucera6, Natalia Mansueto7, Rosalba Caccavale8, Patrizia Del Medico9, Antonella Farina10, Palma Scolieri11, Cecilia Giampietro12, Olga Addimanda13, Riccardo Bixio14, Maddalena Larosa15, Viviana Ravagnani16, Federica Lumetti17, Aldo Biagio Molica Colella17, Elena Bravi17, Rosetta Vitetta17, Bernd Raffeiner17, Gilda Sandri18, Rosario Foti19, Simone Parisi20, Michele Maria Luchetti Gentiloni1, Gianluca Moroncini1. | 1Clinical Medicine, Department of Clinical and Molecular Sciences, Marche Polytechnic University, AOU delle Marche, Ancona; 2Internal Medicine and Rheumatology Unit, University Hospital of Parma, Parma; 3Rheumatology Unit, Clinica Medica Institute, Ospedale SS. Annunziata di Chieti, G.d'Annunzio University of Chieti, Chieti; 4Rheumatology Unit, ARNAS Garibaldi di Catania, Catania; 5Center for the Diagnosis and Therapy of Autoimmune Rheumagological Diseases, Ospedale Santa Rosa, ASL Viterbo, Viterbo; 6Rheumatology Outpatient Unit, ASL Novara, Novara; 7Ambulatori di Reumatologia ASL1 Liguria, Imperia Hospitall, Imperia; 8Department of Clinical, Anesthesiological and Cardiovascular Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome, Polo Pontino, Roma; 9Rheumatology outpatient clinic - Internal Medicine Unit, Civitanova, Marche Hospital, Civitanova, Marche; 10Internal Medicine Unit, Rheumatology outpatient clinic, Ospedale A. Murri di Fermo Fermo; 11Department of Medical Specialties, Nuovo Regina Margherita Hospital, Roma; 12Rheumatology Outpatient Clinic, Azienda ULSS 6 Euganea, Padova, Padova; 13Rheumatology Unit, Azienda Unità Sanitaria Locale di Bologna -- Policlinico S.Orsola- AOU di Bologna, Bologna; 14Rheumatology Unit, IRCCS Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital, Negrar di Valpolicella, Verona; 15Division of Rheumatology - Medical Specialties Department, Ospedale La Colletta-Azienda Sanitaria Locale 3 Genova; 16Rheumatology Unit, Santa Chiara Hospital APSS Trento; 17BIRRA - BIologic Retention Rate in chronic Arthritis - study group Parma; 18Rheumatology Unit, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena; 19Rheumatology Unit, Policlinico San Marco Hospital, Catania; 20Rheumatology Department, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Città della Salute e della Scienza di Torino, Torino, Italy.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
17
Views
0
Downloads