Inflammatory bowel diseases and spondyloarthritis: a focus on female patients

All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
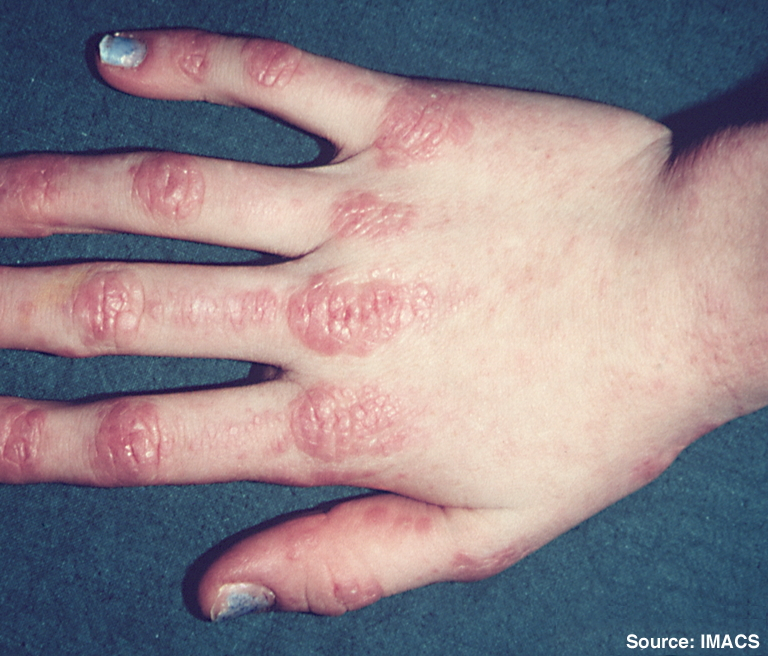
Objective. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease are chronic inflammatory diseases and represent the two most important types of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), while spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises a heterogeneous group of systemic inflammatory chronic rheumatic diseases, including peripheral SpA and axial SpA. Joint manifestations are the most commonly observed extraintestinal manifestations, and they can precede or not the diagnosis of IBD. Notably, in women, misdiagnoses of IBD as irritable bowel syndrome and SpA as fibromyalgia are common, leading to delayed diagnoses, increased disease burden, and poorer prognoses. This narrative review emphasizes the critical role of diagnostic tools in facilitating early referrals of IBD patients with suspected SpA and vice versa to rheumatologists and gastroenterologists, respectively. Special attention is given to the multidisciplinary approach for more effective management of these conditions, particularly in female patients.
Methods. In this narrative review, we critically evaluated the literature on this topic, focusing on papers written in English that address female issues in IBD and SpA.
Results. IBD and SpA are chronic inflammatory disorders often occurring in the same patients. Female patients are often misdiagnosed, and this delay in diagnosis is associated with a higher disease burden and a poorer prognosis.
Conclusions. A multidisciplinary approach is needed to enable early referral between gastroenterologists and rheumatologists, as this means a better prognosis for patients with a reduction in the economic and social burden associated with IBD and SpA.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.