Systemic lupus erythematosus induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor α therapy in inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a case series
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
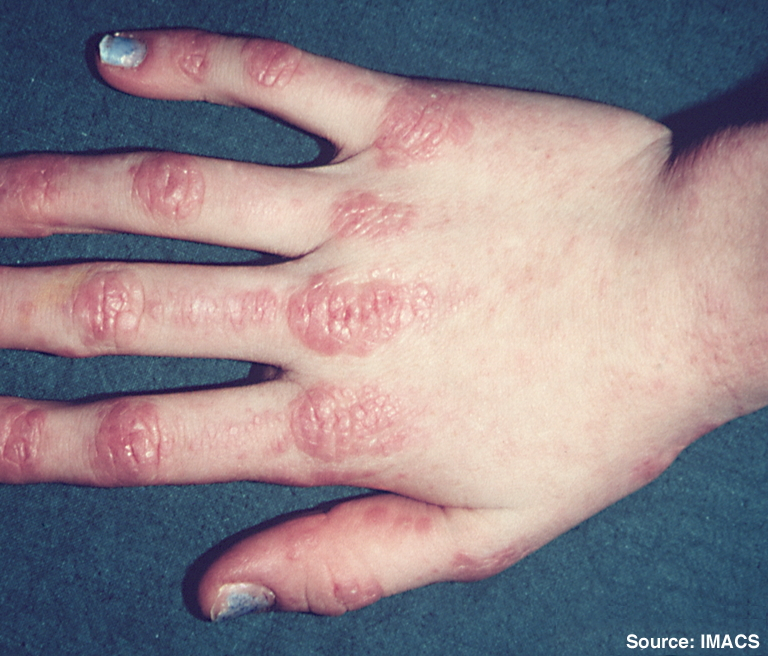
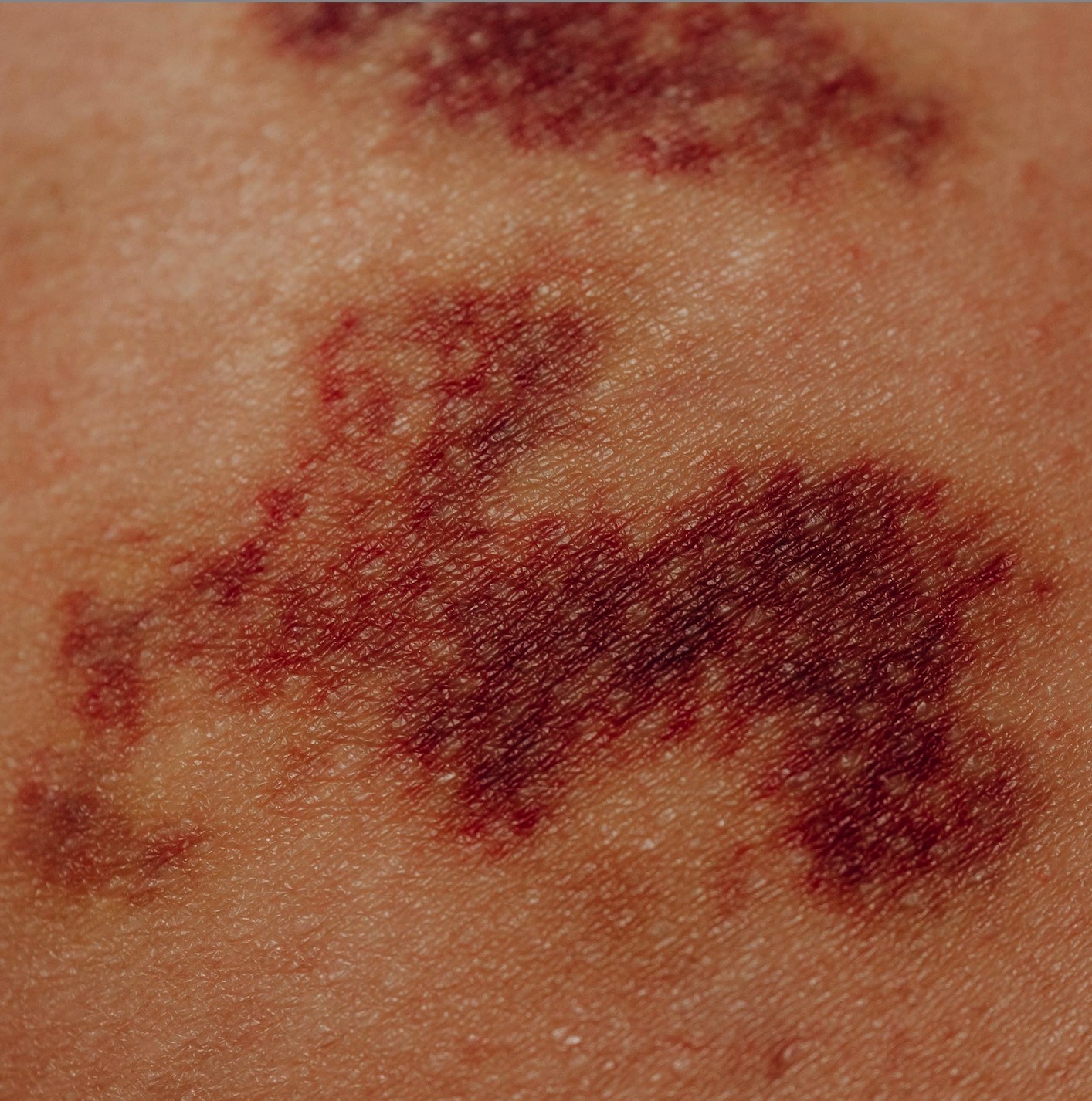
This case series aims to characterize the development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor α (anti-TNFα) therapy in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases, namely rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondylarthritis (SpA), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Patients with a diagnosis of SLE induced by anti-TNFα therapy and registered on the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register (Reuma.pt) who started their first anti-TNFα between 2001 and 2020 were included. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were obtained by consulting Reuma.pt. The diagnosis of SLE induced by anti-TNFα was considered if there was a temporal relationship between the onset of anti-TNFα therapy and manifestations (clinical and immunological) in accordance with the American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism criteria (2019). A total of 607 patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases and six cases of SLE induced by anti-TNF-α therapy were reviewed: two patients were affected by RA, three patients by SpA, and one by PsA. All these patients had articular and constitutional symptoms that improved after discontinuation of the anti-TNFα agent. After switching to a second anti-TNFα agent, there was no recurrence of SLE over time. The development of SLE secondary to anti-TNFα agents in inflammatory rheumatic patients is rare. In this case series, all patients had a mild disease that improved after therapy discontinuation without recurrence of the disease. SLE induced by anti-TNFα should be considered in the follow-up of RA, SpA, and PsA patients.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.