Adrenal hemorrhage and non-ST elevation myocardial infarction: an antiphospholipid syndrome dilemma
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
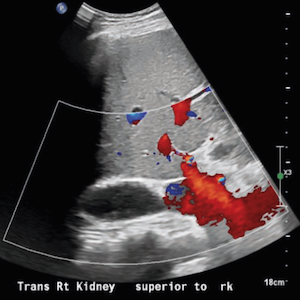
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) can affect different organ systems, including the heart and adrenal glands. Despite being known for its prothrombotic characteristics, APS can have serious bleeding complications. Occasionally, thrombotic and bleeding episodes can present simultaneously in an APS patient. Whenever these events co-occur, resuming anticoagulation becomes a topic of debate. As such, we present the case of a 43-year-old male with triple positive antiphospholipid antibodies, indicating APS, who presented with chest pain. Anticoagulants were switched one month before presentation from warfarin to a direct oral anticoagulant, rivaroxaban. Non-ST elevation myocardial infarction, as well as new-onset left-sided adrenal hemorrhage, were diagnosed. The patient developed adrenal insufficiency; therefore, corticosteroids were administered, and warfarin was resumed to prevent further thrombotic episodes.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.